The recent discovery of a cluster of lost cities in the Amazon rainforest has sparked a wave of excitement and fascination within the archaeological community and beyond.
This groundbreaking finding sheds light on a thriving civilization that once flourished in the heart of the dense Amazonian wilderness, offering a glimpse into the lives of ancient farmers who inhabited this region around 2,000 years ago.
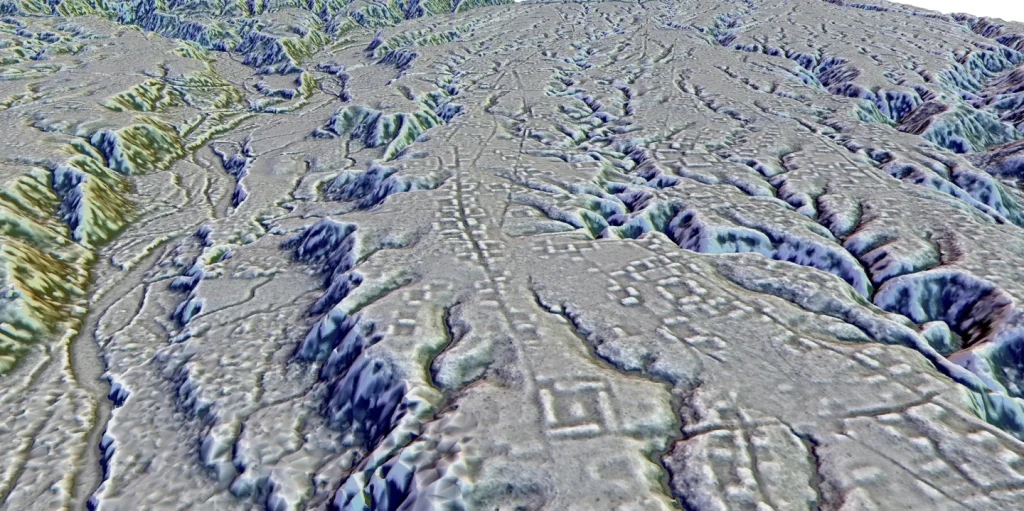
The uncovering of a series of earthen mounds and buried roads in Ecuador has not only unveiled the existence of at least 10,000 farmers but has also unraveled a complex network of settlements and connecting roadways that remained concealed for centuries.
The journey to this remarkable discovery began over two decades ago when archaeologist Stéphen Rostain first noticed the enigmatic earthen structures and roads.
However, it was not until recent advancements in laser-sensor technology that the true extent and significance of these sites were unveiled.
The meticulous mapping of the area revealed a dense network of settlements nestled within the forested foothills of the Andes, painting a vivid picture of a lost valley of cities that thrived for approximately 1,000 years.
This revelation has not only expanded our understanding of ancient civilizations but has also sparked a renewed interest in exploring the untold stories of the past.
The significance of this discovery cannot be overstated. It offers a rare glimpse into a civilization that has long been shrouded in mystery, providing invaluable insights into the social, cultural, and agricultural practices of the ancient inhabitants of the Amazon rainforest.
The presence of such a vast network of settlements and roadways challenges our preconceived notions about the Amazon as a pristine, untouched wilderness, highlighting the rich and complex history that lies hidden beneath its dense foliage.
The implications of this discovery extend far beyond the realm of archaeology. The unearthing of these lost cities has the potential to reshape our understanding of the Amazon rainforest as a dynamic and ever-changing landscape that has been shaped by human activity for millennia.
It underscores the need for a holistic approach to studying and preserving the Amazon, one that takes into account not only its ecological significance but also its rich cultural heritage and historical legacy.
The uncovering of these lost cities serves as a reminder of the boundless potential of archaeological research and the enduring allure of ancient civilizations.
It underscores the importance of continued exploration and preservation efforts in uncovering the untold stories of our past, stories that have the power to reshape our understanding of the world and our place within it.
As we marvel at the intricate network of settlements and roadways that have emerged from the depths of the Amazon rainforest, we are reminded of the resilience and ingenuity of the human spirit.
The legacy of these ancient farmers, who carved out a thriving civilization amidst the lush greenery of the Amazon, serves as a testament to the enduring human quest for knowledge, progress, and connection with the natural world.
In conclusion, the discovery of a cluster of lost cities in the Amazon rainforest stands as a testament to the enduring allure of ancient civilizations and the boundless potential of archaeological research.
It offers a rare glimpse into the lives of ancient farmers who once inhabited this region, unraveling a complex network of settlements and roadways that have remained concealed for centuries.
This groundbreaking finding not only expands our understanding of ancient civilizations but also underscores the need for a holistic approach to studying and preserving the Amazon rainforest.
As we continue to unravel the untold stories of our past, we are reminded of the enduring legacy of human ingenuity and the profound connection between humanity and the natural world.
The recent discovery of a cluster of lost cities in the Amazon rainforest has sparked a wave of excitement and fascination within the archaeological community and beyond.
This groundbreaking finding sheds light on a thriving civilization that once flourished in the heart of the dense Amazonian wilderness, offering a glimpse into the lives of ancient farmers who inhabited this region around 2,000 years ago.
The uncovering of a series of earthen mounds and buried roads in Ecuador has not only unveiled the existence of at least 10,000 farmers but has also unraveled a complex network of settlements and connecting roadways that remained concealed for centuries.
The journey to this remarkable discovery began over two decades ago when archaeologist Stéphen Rostain first noticed the enigmatic earthen structures and roads.
However, it was not until recent advancements in laser-sensor technology that the true extent and significance of these sites were unveiled.
The meticulous mapping of the area revealed a dense network of settlements nestled within the forested foothills of the Andes, painting a vivid picture of a lost valley of cities that thrived for approximately 1,000 years.
This revelation has not only expanded our understanding of ancient civilizations but has also sparked a renewed interest in exploring the untold stories of the past.
The significance of this discovery cannot be overstated. It offers a rare glimpse into a civilization that has long been shrouded in mystery, providing invaluable insights into the social, cultural, and agricultural practices of the ancient inhabitants of the Amazon rainforest.
The presence of such a vast network of settlements and roadways challenges our preconceived notions about the Amazon as a pristine, untouched wilderness, highlighting the rich and complex history that lies hidden beneath its dense foliage.
The implications of this discovery extend far beyond the realm of archaeology. The unearthing of these lost cities has the potential to reshape our understanding of the Amazon rainforest as a dynamic and ever-changing landscape that has been shaped by human activity for millennia.
It underscores the need for a holistic approach to studying and preserving the Amazon, one that takes into account not only its ecological significance but also its rich cultural heritage and historical legacy.
The uncovering of these lost cities serves as a reminder of the boundless potential of archaeological research and the enduring allure of ancient civilizations.
It underscores the importance of continued exploration and preservation efforts in uncovering the untold stories of our past, stories that have the power to reshape our understanding of the world and our place within it.
As we marvel at the intricate network of settlements and roadways that have emerged from the depths of the Amazon rainforest, we are reminded of the resilience and ingenuity of the human spirit.
The legacy of these ancient farmers, who carved out a thriving civilization amidst the lush greenery of the Amazon, serves as a testament to the enduring human quest for knowledge, progress, and connection with the natural world.
In conclusion, the discovery of a cluster of lost cities in the Amazon rainforest stands as a testament to the enduring allure of ancient civilizations and the boundless potential of archaeological research.
It offers a rare glimpse into the lives of ancient farmers who once inhabited this region, unraveling a complex network of settlements and roadways that have remained concealed for centuries.
This groundbreaking finding not only expands our understanding of ancient civilizations but also underscores the need for a holistic approach to studying and preserving the Amazon rainforest.
As we continue to unravel the untold stories of our past, we are reminded of the enduring legacy of human ingenuity and the profound connection between humanity and the natural world.
The Upano people, who inhabited the settlements between approximately 500 B.C. and 300 to 600 A.D., have left an indelible mark on history.
This period of their occupation coincided with the height of the Roman Empire in Europe, a testament to the rich and diverse tapestry of human civilization across the globe.
Recent research has shed light on the remarkable achievements of the Upano people, revealing a sophisticated society characterized by impressive urban planning, agricultural innovation, and a densely populated landscape.
The remnants of this ancient civilization tell a compelling story of ingenuity and communal organization. The residential and ceremonial buildings, constructed on over 6,000 earthen mounds, stand as a testament to the architectural prowess of the Upano people.
These structures were complemented by expansive agricultural fields, carefully tended with the aid of drainage canals.
The scale of their engineering feats is further underscored by the presence of roads that were a remarkable 33 feet (10 meters) wide and stretched for 6 to 12 miles (10 to 20 kilometers).
Such infrastructure speaks to a society that was not only adept at harnessing the land for sustenance but also at facilitating communication and trade across vast distances.
Estimating the population of these settlements is a challenging endeavor, yet it is clear that they were home to a substantial number of individuals.
The lower estimates suggest a population of at least 10,000 inhabitants, while the peak may have seen numbers swell to 15,000 or even 30,000.
These figures are comparable to the estimated population of Roman-era London, then Britain’s largest city, highlighting the sheer magnitude of the Upano settlements.
The density of occupation and the complexity of their society are further emphasized by comparisons to contemporaneous societies, with experts noting that the Upano settlements stand in a class of their own in terms of their early development and sophistication.
The discoveries surrounding the Upano settlements offer a window into a world that thrived in a remote era, showcasing the resilience and adaptability of human communities.
The intricate network of mounds, fields, and roads speaks to a society that was not only capable of sustaining itself but also of thriving and evolving in a challenging environment.
The findings of this research prompt us to reconsider our understanding of ancient civilizations and the remarkable achievements that have shaped our collective history.
In conclusion, the Upano settlements represent a remarkable chapter in the annals of human civilization. Their accomplishments in urban planning, agriculture, and societal organization stand as a testament to the ingenuity and resourcefulness of the Upano people.
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of their past, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and complexity of human societies throughout the ages.
The legacy of the Upano settlements serves as a poignant reminder of the enduring impact of ancient civilizations and the invaluable insights they offer into the human experience.
The recent findings in the Amazon have shed new light on the complexity of the region’s ancient civilizations. José Iriarte, an archaeologist at the University of Exeter, has highlighted the elaborate system of organized labor that would have been required to build the roads and thousands of earthen mounds in the Amazon.
This challenges the traditional view of the Amazon as a pristine wilderness with only small groups of people.
Iriarte’s observations about the building materials used by the ancient Amazonians further emphasize the immense amount of labor that went into constructing these structures.
While the Incas and Mayans built with stone, the people in the Amazon relied on mud due to the lack of readily available stone.
This underscores the advanced engineering and construction techniques employed by the ancient Amazonians, as well as their ability to adapt to their environment.
Moreover, the discovery of intricate rainforest societies that predated European contact in other parts of the Amazon, such as Bolivia and Brazil, adds to the growing body of evidence that challenges the simplistic view of the region’s history.
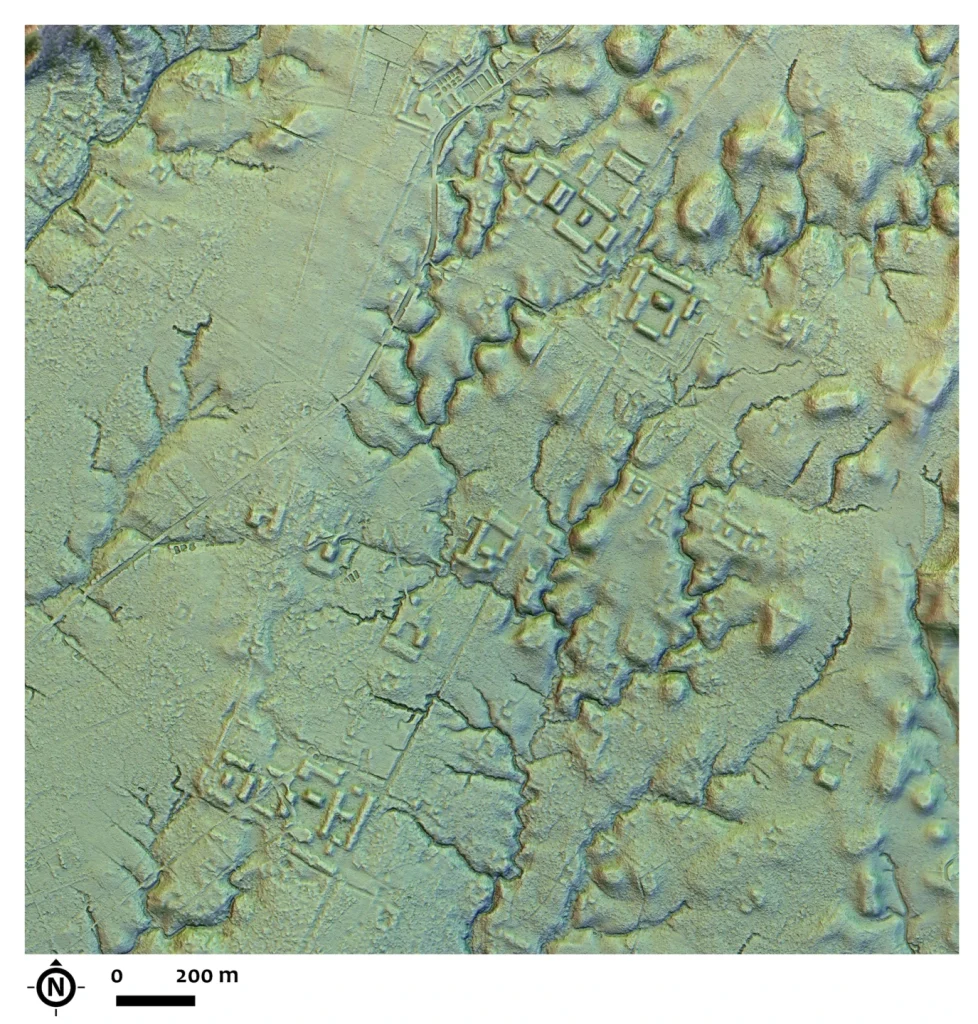
These findings demonstrate that the Amazon has always been home to a diverse range of people and settlements, each with their own unique way of life.
The implications of these discoveries are profound. They force us to reevaluate our understanding of the Amazon and its inhabitants, and to recognize the rich and complex history of the region.
The traditional narrative of the Amazon as a sparsely populated wilderness is being replaced by a more nuanced and dynamic picture of ancient Amazonian societies.
As we continue to uncover more about the ancient civilizations of the Amazon, it is crucial to approach this research with an open mind and a willingness to challenge our preconceived notions.
The Amazon is not simply a pristine wilderness, but a region with a rich and diverse history that is still being uncovered.
In conclusion, the recent discoveries in the Amazon have revealed the intricate and complex nature of its ancient civilizations.
The elaborate system of organized labor, advanced construction techniques, and evidence of diverse societies challenge the traditional view of the region as a pristine wilderness.
As we continue to learn more about the ancient Amazonians, it is important to approach this research with an open mind and a willingness to embrace the complexity of the region’s history.